The main difference between lytic cycle and lysogenic cycle is that lytic cycle destroys the host cell whereas lysogenic cycle does not destroy the host cell. Describe the difference between the bacteriophage lytic and lysogenic cycle.
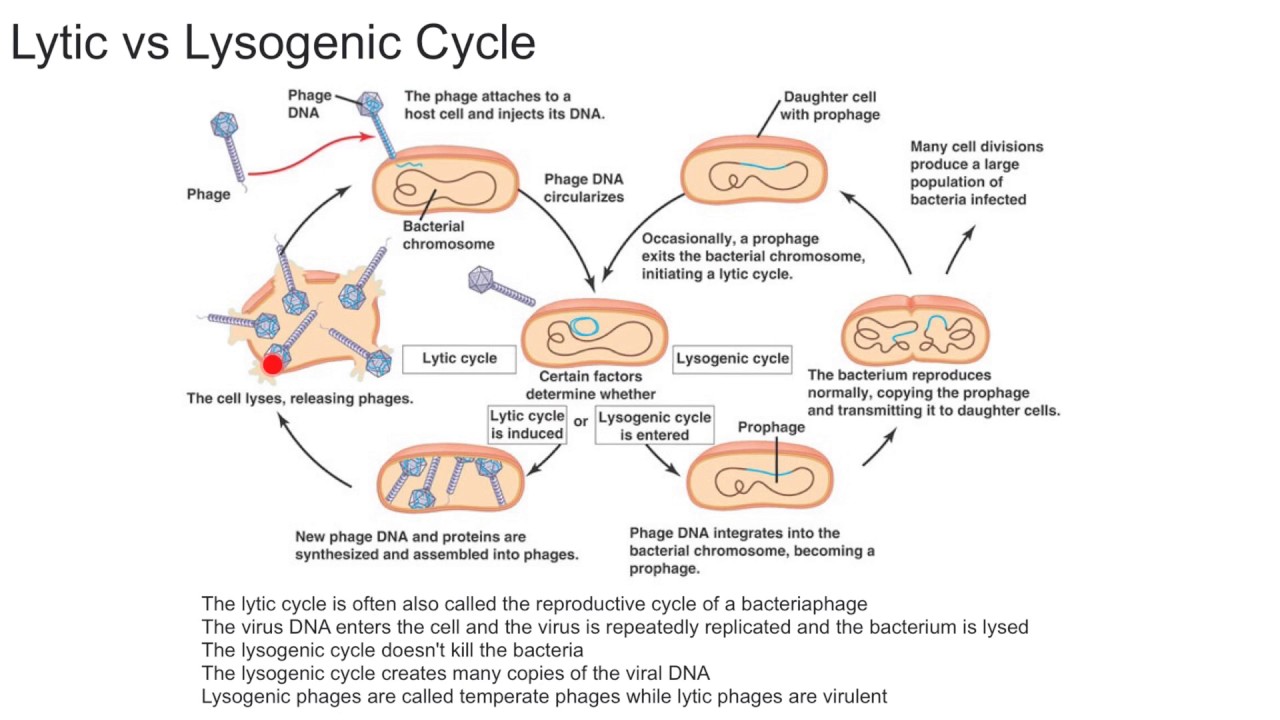
Lytic Vs Lysogenic Cycle Youtube
In the lytic cycle the bacteriophage exists as viral DNA free in the bacterial host cells cytoplasm.

. However in the lysogenic cycle viral DNA may merge with the host DNA. The viral DNA directs the production of new viral particles by the host cell until the virus kills the cell by lysis. Lytic cycle or lytic phages called as virulent phages multiplies inside the host bacterium and new viral particles comes out by lysing or by rupturing the host bacterial cell wall.
The lysogenic cycle Figure 3 sometimes referred to as temperate or non-virulent infection does not kill the host cell instead using it as a refuge where it exists in a dormant state. Start your trial now. The host cell will die because the virus exits the cell bc the skeleton will move inward.
Article shared by. Following the injection of the phage DNA into the host cell it integrates itself into the host genome with the help of phage-encoded integrases where it is then termed a prophage. While the lysogenic cycle can sometimes happen in eukaryotes prokaryotes or bacteria are much better understood examples.
In this cyclephage DNA becomes integrated with the bacterial genome and replicates with the. A bacteriophage is a virus that infects bacteria. The following are the steps of the lysogenic cycle1 Viral genome enters cell2 Viral genome integrates into Host cell genome3 Host cell DNA Polymerase copies viral chromosomes4 cell divides and virus chromosomes are transmitted to cells daughter cells5 At any moment when the virus is triggered the viral.
Solution for Describe the difference between the bacteriophage lytic and lysogenic cycle. The bacteriophage will lie dormant in the lysogenic cycle unless it is triggered to enter the lytic cycle possibly by sensing that the bacterial cell. Lets take a closer look at each of these cycles.
Also known as temperate cycle. Virals cell dna becomes dormant. The phage infects a bacterium and inserts its DNA into the bacterial chromosome allowing the phage DNA now called a prophage to be copied and passed on along with the cells own DNA.
Virus latency or viral latency is the ability of a pathogenic virus to lie dormant latent within a cell denoted as the lysogenic part of the viral life cycle. T phages T2 T4 T6 etc. This affects the phenotype of the infected.
After the lysis of host cells. The phage first attaches to the host cell and injects its DNA. Lysogenic cycle or lysogenic phages called as temperate phages does not undergo multiplication or induce lysis here the viral DNA.
Lysogenic conversion involves the infection of a bacterium by a bacteriophage and the expression of the bacteriophage genes that are in the prophage. The question asks to explain the ETC as a whole. In the lysogenic cycle the bacteriophage DNA is integrated into the.
In the lysogenic cycle the DNA is only replicated not translated into proteins. April 26 2018 Posted by DrSamanthi. A bacterial host with a prophage is called a lysogen and then the entire process in which a bacterium is infected by a temperate phage is called lysogeny.
The key difference between lytic and lysogenic cycle of bacteriophage is that during lytic cycle of bacteriophage reproduction the bacteriophage that enters the host cell present as a separate component without integrating with the host DNA while in lysogenic cycle the bacteriophage DNA is integrated into the host. The difference between lysogenic and lytic cycles is that in lysogenic cycles the spread of the viral DNA occurs through the usual prokaryotic reproduction whereas a lytic cycle is more immediate in that it results in many copies of the virus being created very quickly and the cell is. Recommended textbook explanations Biology.
In this cycle intra-cellular multiplication of the phage results in the lysis of host bacteria resulting in release of progeny virions. This cycle begins much like the lytic cycle. Difference between lytic and lysogenic cycles is that lytic cycle destroys the host cell whereas Lysogenic Cycle does not.
The viral DNA destroys DNA of the host cell halting the cells functioning in Lytic Cycle. When large numbers of bacteriophages are present they can enter an alternative replication mode the lysogenic cycle where phages can reproduce without killing their host. Then the DNA polymerase copies chromosomes and the cell divides and the virus is transmitted into the daughter cells.
In the lytic cycle the DNA is multiplied many times and proteins are formed using processes stolen from the bacteria. Page 1 fLytic and lysogenic cycles of a bacteriophage. Also known as virulent cycle.
Phages exhibit two different types of life cycle. First week only 499. Lytic and Lysogenic Cycles are two viral replication processes that can occur simultaneously.
The host cell is not destroyed. The action of most of viral genes is to enable the viruses to infect their respective host cells multiply by using the host machinery such as enzymes and ribosomes and then causing the lysis of cells. However once inside the phage DNA recombines and integrates with the bacterial genome.
Viral DNA destroys the host cell DNA and arrests the cell functions in the lytic cycle. Terms in this set 30 The difference between Lytic cycle and the Lysogenic cycle. April 17 2022.
Two major cycles of multiplication of bacteriophages are. The lysogenic cycle starts off the same but is different in the sense that it integrates with the host cell. How are viral latency and lysogeny related.
When those cells reproduce they create more cells with the same virus. 9 rows Lytic cycle comparitively more common is a method of viral multiplication wherein the virus. A latent viral infection is a type of persistent viral infection which is distinguished from a chronic.
During the lysogenic cycle instead of killing the host the phage genome which is called a prophage integrates itself to the bacterial chromosome and becomes part of the host.

The Lytic And Lysogenic Cycles Of Bacteriophage Infection By Viral Dna Download Scientific Diagram
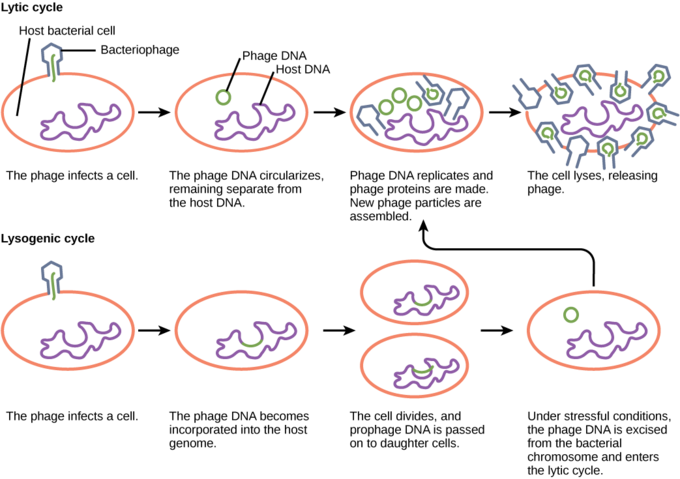
21 2b The Lytic And Lysogenic Cycles Of Bacteriophages Biology Libretexts

The Lysogenic And Lytic Cycle Of Bacteriophages The Lysogenic And Download Scientific Diagram
0 Comments